Acinic cell carcinoma
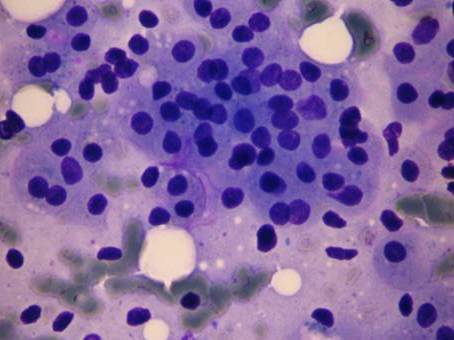
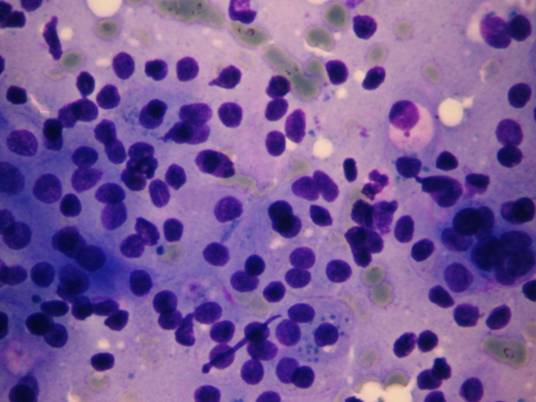
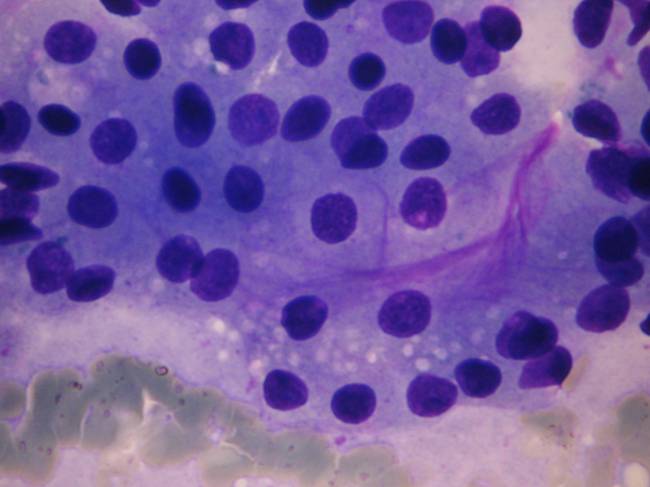
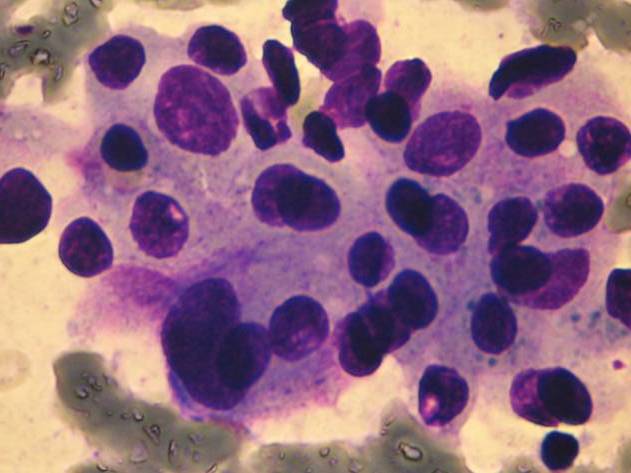
Acinic cell carcinoma occurs most frequently in the parotid gland. The former name was 'acinic cell tumor' because in some cases only very mild atypia is present. 2 – 7% of all salivary gland tumors belong to this group.
There are four patterns: solid, microcystic, papillary-cystic, follicular. Four cell types are usually found in this tumor: acinar cells, clear cells, intercalated duct-like cells, vacuolated cells. All patterns and all cells are usually present in the same tumor, some of them may predominate. The tumor is more common in women and it may occurr in very young age as well. The different cell types are identified in the cytologic smear. The tumor is usually infiltrated by many lymphocytes, which is an important diagnostic feature. In this case the cytologic picture is similar to that of a well-differentiated adenocarcinoma metastatic to a lymph node. In case well-differentiated acinic cells are seen without any ductal elements, you always have to think of an acinic cell carcinoma, even if the patient is very young.